clc;
clear all;
close all;
include_gblrefs;
init_constants;
[K,F,D] = preProcessor;
fprintf(1,'Assembling stiffness matrix...\n');
for e = 1:nel
ke = elemStiffMtx(e);
K = drvAssembleMtx(K,e,ke);
end
fprintf(1,'Assembling forcing vector...\n');
F = drvPointLoads(F);
F = drvEdgeLoads(F);
F = drvAreaLoads(F);
fprintf(1,'Solving system of equations...\n');
[D,F] = drvSolveEqnSystem(neq,neqfree,K,F,D);
posProcessor(D);
fprintf(1,'Finished.\n');
Pre-processing...
Assembling stiffness matrix...
Assembling forcing vector...
Solving system of equations...
Preparing post-processing data...
Displaying results...
Finished.
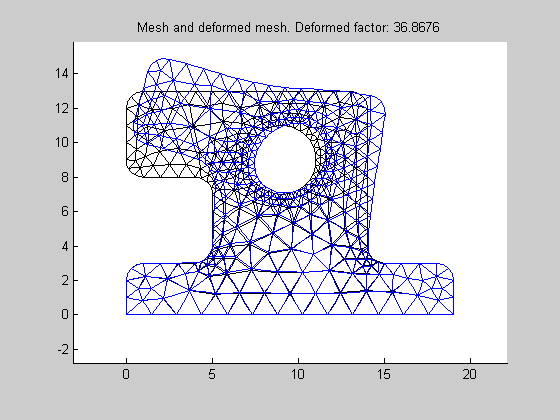
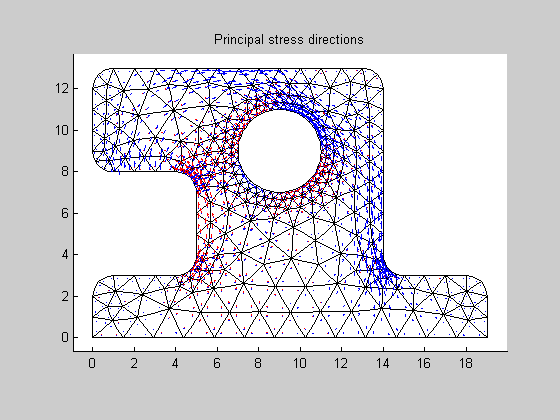
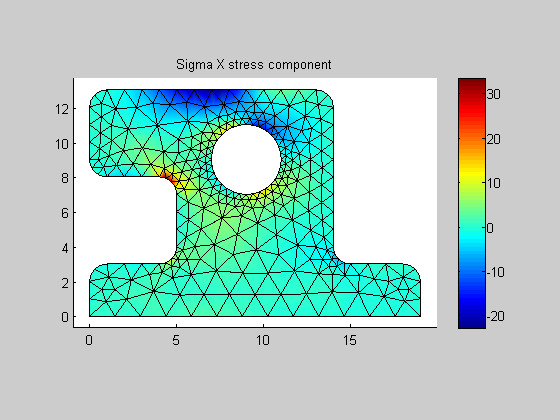
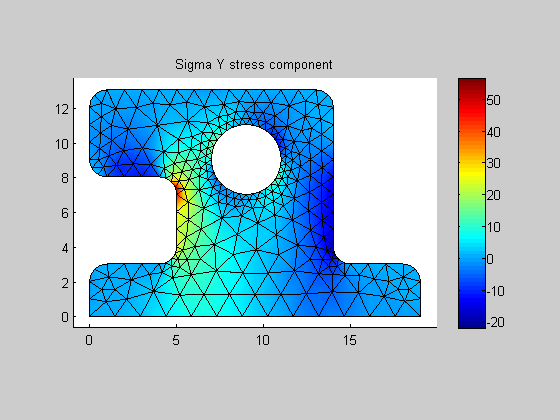
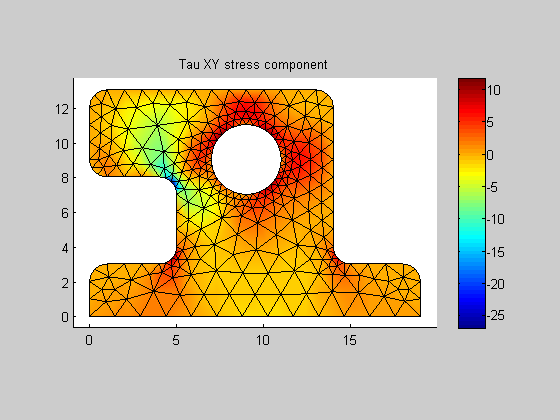
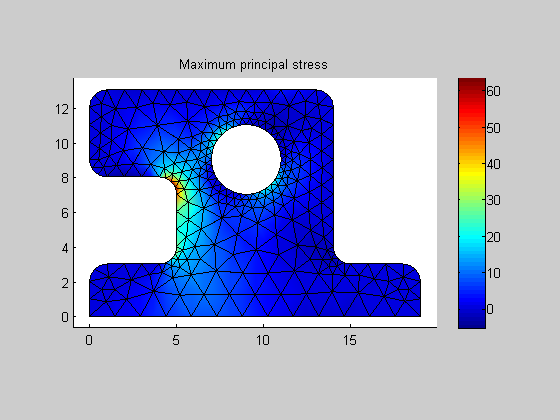
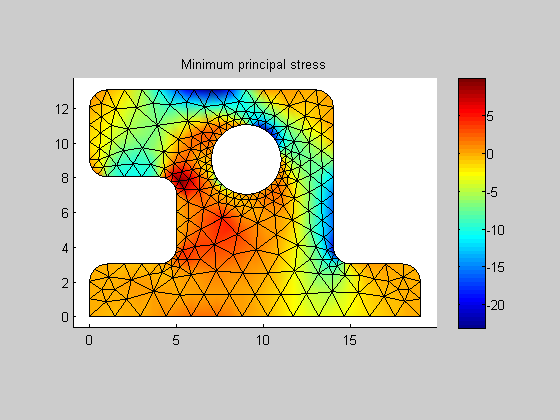
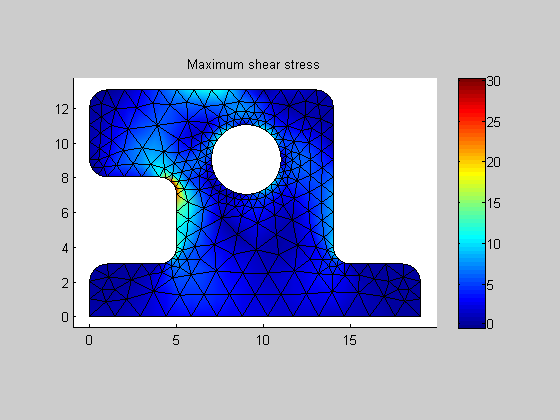
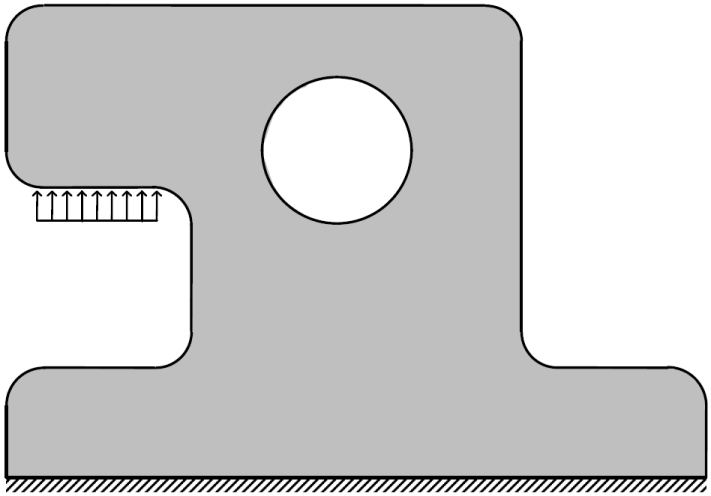
Resultados do exemplo LatchT6.nf
| main |
Main driver and global variable files.
|
| main |
elasticity2D - FEM
Main driver file.
This file contains MATLAB code of a program for linear-elastic,
displacement-based, two-dimensional, finite-element analysis for
solving a stress-distribution elasticity problem.
The program reads a file with FE model data, in a neutral format,
assembles a system of equations, solves the system and visualizes
the response data.
|
| include_gblrefs |
File to include global variables
|
| init_constants |
Initialize constant global variables.
|
| pre |
Pre-processing files.
|
| preProcessor |
Preprocessing input data and sets up mesh information.
Output arguments:
K: global stiffness matrix (returns initialized with null values)
F: global forcing vector (returns initialized with null values)
D: global displacement vector (returns initialized with null values
and with known support settlement values)
|
| input_patchtest_q4 |
Input data for patch test with 4 QUAD4 elements in a irregular mesh.
There are prescribed displacaments in x direction and
applied tractions in y direction.
8
7 +----+--------------+ 9
| \ |
| \ --- |
| --- \ | 4 | |
| | 3 | \ --- |
| --- \ -+ 6
| \ 5 --/ |
4 +-----------+--/ |
| --- / |
| | 1 | / --- |
| --- / | 2 | |
| / --- |
1 +------+------------+ 3
2
|
| preReadNF |
This fuction reads a neutral-format file with input data for a finite-element model for this program.
The neutral format is described in www.tecgraf.puc-rio.br/neutralfile.
It is assumed that all nodes and elements are numbered consecutively from
one to the total number of nodes and elements.
It is assumed that there is only one type of element and only one
type of gauss integration order in each finite element model.
It is assumed that there is a single load case.
|
| node |
Node files.
|
| nodeSetupDOFNum |
Setup global d.o.f numbering matrix.
Free d.o.f.'s are numbered first.
Counts total number of equations of free d.o.f.'s and total number
of equations of fixed d.o.f.'s, and stores in global variables.
Incomplete file. Need to complete in:
%%% COMPLETE HERE 01 %%%
%%% COMPLETE HERE 02 %%%
|
| shp |
Finite-element shape files.
|
| shpNodeCCWOrder |
Returns the resequence vector of nodal indices of an element in CCW order.
Output arguments:
rv: resequence vector of nodal indices of an element in CCW order
|
| shpNodeParCoords2D |
Returns the parametric coordinates of the nodal points of an element.
Output arguments:
pt: array with pairs of element nodal paramatric coordinates
|
| shpNmatrix2D |
Evaluates 2D shape function matrix.
Evaluates shape functions (in parametric coordinates) at point (r,s)
for 2D elements.
Input arguments:
r: first parametric coordinate value
s: second parametric coordinate value
Output arguments:
N: shape function matrix evaluated at given position
Incomplete file. Need to complete in:
%%% COMPLETE HERE 03 %%%
%%% COMPLETE HERE 04 %%%
%%% COMPLETE HERE 05 %%%
|
| shpGradNmatrix2D |
Evaluates derivatives of shape functions (in parametric coordinates).
Input arguments:
r,s: parametric coordinate values
Output arguments:
GradN: Shape function gradient matrix evaluated at given position
Incomplete file. Need to complete in:
%%% COMPLETE HERE 06 %%%
%%% COMPLETE HERE 07 %%%
%%% COMPLETE HERE 08 %%%
|
| shpDetJ2D |
Evaluates 2D Jacobian determinant.
Evaluates determinant of Jacobian matrix of parametric to cartesian
transformation at point (r,s) in parametric coordinates.
Input arguments:
r,s: parametric coordinate values
C: nodal coordinate matrix
Output arguments:
detJ: determinant of Jacobian matrix evaluated at given position
Incomplete file. Need to complete in:
%%% COMPLETE HERE 09 %%%
|
| shpGetEdge |
Get nodal incidence on a given 2D element edge (side).
Input arguments:
e: element number
nod1: first node on element edge
nod2: last node on element edge
Output arguments:
nne: number of nodes of target element edge
IENe: local nodal connectivity array of target element edge
|
| shpNmatrix1D |
Evaluates 1D shape function matrix.
Evaluates shape functions (in parametric coordinate) at point (r)
for 1D elements.
Input arguments:
r: parametric coordinate value
Output arguments:
N: shape function matrix evaluated at given position
|
| shpDetJ1D |
Evaluates 1D (edge) Jacobian determinant.
Evaluates determinant of Jacobian matrix of parametric to cartesian
transformation at point (r) in parametric coordinate.
Input arguments:
r: parametric coordinate value
C: nodal coordinate matrix
Output arguments:
detJ: determinant of Jacobian matrix evaluated at given position
|
| gauss |
Gauss quadrature files.
|
| gauss |
Get gauss points coordinates in the parametric space of element and corresponding weights for a given quadrature type and order.
Input arguments:
type: gauss quadrature type (either line, triangle or quadrilateral)
order: quadrature order
Output arguments:
ngp: number of gauss points
w: array of gauss point weights
gp: array of gauss point parametric coordinates
Incomplete file. Need to complete in:
%%% COMPLETE HERE 10 %%%
%%% COMPLETE HERE 11 %%%
%%% COMPLETE HERE 12 %%%
%%% COMPLETE HERE 13 %%%
|
| anm |
Analysis model files.
|
| anmEMtx |
Generate material constituive matrix for a given element.
The material constitutive matrix is assembled using the
element modulus of elasticity and poisson ratio.
The matrix size and layout depends on the type of analysis.
For plane stress and plane strain analysis, the size is (3,3).
For axisymmetric analysis, the size is (4,4).
Input arguments:
e: index of element
Incomplete file. Need to complete in:
%%% COMPLETE HERE 14 %%%
%%% COMPLETE HERE 15 %%%
%%% COMPLETE HERE 16 %%%
|
| anmBMtx |
Assemble 2D B matrix for an element.
Evaluates derivatives of shape functions (in physical Cartesian coordinates)
at point (r,s) in parametric coordinates and assembles them in the B matrix.
In case of axisymmetric analysis, the shape function itself is also used.
Input arguments:
r,s: parametric coordinate values
C: nodal coordinate matrix
Output arguments:
B: B matrix evaluated at given position
Incomplete file. Need to complete in:
%%% COMPLETE HERE 17 %%%
%%% COMPLETE HERE 18 %%%
%%% COMPLETE HERE 19 %%%
|
| anmPointStress |
Get stress components (sigma x, sigma y and tau xy) at a given point on an element.
For axisymmetric analysis the sigma z stress component is desregarded.
Input arguments:
r,s: parametric coordinate values of point location
C: nodal coordinate matrix of target element
E: constituive matrix of target element
d: generalized displacements/rotations for all d.o.f.'s of element
Output arguments:
str: stress components (sx,sy,txy) at target point
Incomplete file. Need to complete in:
%%% COMPLETE HERE 20 %%%
|
| elem |
Finite element files.
|
| elemStiffMtx |
Generate stiffness matrix for a given element.
Input arguments:
e: index of target element
Incomplete file. Need to complete in:
%%% COMPLETE HERE 21 %%%
|
| elemAreaENL |
Generate equivalent nodal load vector (feq) for an area uniform distributed load (qx,qy) on a given element.
Input arguments:
e: element number
q: area uniform distributed load values: q(ndof,1)
Output arguments:
nne: number of nodes of equivalent nodal load vector
IENe: local nodal connectivity array of equivalent nodal load
feq: equivalent nodal load vector
Incomplete file. Need to complete in:
%%% COMPLETE HERE 22 %%%
|
| elemEdgeENL |
Generate equivalent nodal load vector (feq) for an edge uniform distributed load (px,py) on a given element side.
Input arguments:
e: element number
nod1: first node on element edge
nod2: last node on element edge
p: edge uniform distributed load values: p(ndof,1)
Output arguments:
nne: number of nodes of equivalent nodal load vector
IENe: local nodal connectivity array of equivalent nodal load
feq: equivalent nodal load vector
Incomplete file. Need to complete in:
%%% COMPLETE HERE 23 %%%
|
| elemGaussStress |
Get stress components at gauss points and gauss point cartesian coordinates for a given element.
Input arguments:
D: solution vector: generalized displacements/rotations for all d.o.f.'s
e: target finite element index
Output arguments:
ngp: number of gauss points for stress evaluation
str: stress components (sx,sy,txy) at each gauss point
gpc: gauss point cartesian coordinates array
Incomplete file. Need to complete in:
%%% COMPLETE HERE 24 %%%
|
| elemTRMtx |
Compute gauss-to-node results transfer matrix (TR matrix).
Refs.:
Hinton & Campbell, "Local and Global Smoothing of Discontinous Finite
Element Functions using a Least Squares Method", Int. J. Num. Meth. Engng.,
Vol. 8, pp. 461-480, 1974.
Burnett, D.S., "Finite Element Analysis - From Concepts to Applications",
Addison-Wesley, 1987.
Martha, L.F., "Notas de Aula do Curso CIV 2118 - Metodo dos Elementos
Finitos", 1994.
This functions loads global variables TR and n_gaussstress_pts
(see file include_gblrefs.m).
|
| drv |
Analysis driver files.
|
| drvAssembleMtx |
Assemble global stiffness matrix.
Input/output arguments:
K: global stiffness matrix
Input arguments:
e: element number
ke: element local stiffness matrix
Incomplete file. Need to complete in:
%%% COMPLETE HERE 25 %%%
|
| drvPointLoads |
Add point (nodal) loads to global forcing vector.
Add nodal load components to any term of the global forcing vector,
incluing the terms that correspond to constrained d.o.f.
Input/output arguments:
F: global forcing vector
Incomplete file. Need to complete in:
%%% COMPLETE HERE 26 %%%
%%% COMPLETE HERE 27 %%%
|
| drvAreaLoads |
Add area (element) equivalent nodal loads to global forcing vector.
Input/output arguments:
F: global forcing vector
|
| drvEdgeLoads |
Add edge (element side) equivalent nodal loads to global forcing vector.
Input/output arguments:
F: global forcing vector
|
| drvAssembleENL |
Add equivalent nodal load vector to the global forcing vector.
Assemble the given equivalent nodal load vector to any term of
the global forcing vector, incluing the terms that correspond
to constrained d.o.f.
Input/output arguments:
F: global forcing vector
Input arguments:
nne: number of nodes of given equivalent nodal load vector
IENe: array of nodes of given equivalent nodal load
feq: equivalent nodal load vector
Incomplete file. Need to complete in:
%%% COMPLETE HERE 28 %%%
%%% COMPLETE HERE 29 %%%
|
| drvSolveEqnSystem |
Partition and solve the system of equations.
Input arguments:
neq: total number of equations
neqfree: number of equations of free d.o.f.'s
K: global stiffness matrix
Input/Output arguments:
F: global force vector (right hand side)
D: global displacement vector
|
| pos |
Post-processing files.
|
| posProcessor |
Visualize mesh and results of current analysis.
Input arguments:
D: global displacement vector
|
| posPrincStress |
Get principal stress components and orientation for a given stress tensor.
Input arguments:
str: stress tensor (sx, sy, txy) stored in a column vector.
Output arguments:
prc: principal stress components (s1, s2, taumax) stored in a column vector.
thetap: angle of normal of principal stress plane w.r.t x axis (angle is
returned in radians from 0 to 180 degrees).
|
| posGaussStresses |
Create arrays and compute gauss stress components and principal stresses for all elements.
Input arguments:
D: solution vector: generalized displacements/rotations for all d.o.f.'s
All gauss point location and stress arrays are declared as global variables
(see file incinclude_gblrefs.m).
|
| posElemStressesExtrap |
Create arrays and compute node extrapolated stress components and principal stressesfor all elements.
The nodal stress components are computed by extrapolation of gauss point
stress components using the TR matrix (which is a global variable that is
assumed already created).
All stress arrays are declared as global variables
(see file include_gblrefs.m).
|
| posNodeStressesExtrap |
Create arrays and compute extrapolated node smoothed stress components and principal stresses for all nodes.
The nodal stress components are computed by averaging values of element
extrapolated nodal stress components of all elements adjacent to each node.
All stress arrays are declared as global variables
(see file include_gblrefs.m).
|
| posCreateFigs |
Creates figures for post-processing results.
Eight windows are created and positioned on the screen.
Each window plots a type of post-process result.
|
| posPlotMesh |
Plots mesh in current active figure.
|
| posPlotDeformMesh |
Plots deformed mesh in current active figure.
|
| posPlotNodeContour |
Plots current active node contour response in current active figure.
|