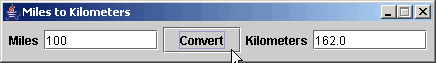
This program converts miles into kilometers. It provides a basic plan for making a program that, when a button is pressed, takes input from a field, computes a new value based on that, and puts the result in another field. Extending this program is the basis for many other examples. To customize it:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 |
// GenericCalc.java - Input field, button, output field generic program.
// Fred Swartz, 2004-10-25
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.event.*;
////////////////////////////////////////////////////// class GenericCalc
class GenericCalc {
//====================================================== method main
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame window = new GenericCalcGUI();
window.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
window.setVisible(true);
}
}
/////////////////////////////////////////////////// class GenericCalcGUI
class GenericCalcGUI extends JFrame {
//=============================================== instance variables
private JTextField m_milesTf = new JTextField(10);
private JTextField m_kilometersTf = new JTextField(10);
private JButton m_convertBtn = new JButton("Convert");
//====================================================== constructor
public GenericCalcGUI() {
//... Add a listener to the button
m_convertBtn.addActionListener(new ConvertListener());
//... Create content panel, set layout, add components
JPanel content = new JPanel();
content.setLayout(new FlowLayout()); // use FlowLayout
content.add(new JLabel("Miles")); // create and add label
content.add(m_milesTf); // add input field
content.add(m_convertBtn); // add button
content.add(new JLabel("Kilometers")); // create and add label
content.add(m_kilometersTf); // add output field
//... Set window characteristics
this.setContentPane(content);
this.pack();
this.setTitle("Miles to Kilometers");
this.setResizable(false);
}//end constructor
///////////////////////////////////////// inner class ConvertListener
class ConvertListener implements ActionListener {
//============================================= actionPerformed
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// This only copies input field to output field.
String in = m_milesTf.getText(); // get input
double mi = Double.parseDouble(miles);
double km = convertMilesToKilometers(mi);
m_kilometersTf.setText("" + km); // set output
}
}//end class ConvertListener
//=========================================== convertMilesToKilometers
// Performing the pure logic of the program (often called the model)
// is typically done in a separate class.
// Here we only put it into a separate method.
// You might think this is too trivial to put into a method.
// Perhaps in this case, but it is a very good habit to
// acquire because in "real" programs there will be
// a big payoff in clarity.
public double convertMilesToKilometers(double miles) {
return mi * 1.62;
}
}//endclass GenericCalcGUI
|