#include <stdlib.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <math.h>#include "geo.h"#include "pfs.h"#include "amr3b.h"

Go to the source code of this file.
Data Structures | |
| struct | PfsElem |
| struct | PfsAdjNode |
| struct | PfsNode |
| struct | PfsSurf |
| #define | _PFS_C |
| #define | ITER_TOLER 0.0001 |
| #define | TOLER 1e-5 |
| #define | COL_TOLER 1e-5 |
| #define | ABS(x) (((x) < 0.0)? -(x): (x)) |
| #define | MAX(a, b) (((a) > (b)) ? (a) : (b)) |
| #define | Len2(x, y) sqrt((double)(((x)*(x))+((y)*(y)))) |
| #define | Len3(x, y, z) sqrt((double)(((x)*(x))+((y)*(y))+((z)*(z)))) |
| #define | DET2D(a, b, c, d) (((a)*(d))-((b)*(c))) |
| #define | X_CROSS_LINE_LINE(x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4) |
| #define | Y_CROSS_LINE_LINE(x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4) |
| #define | X_CROSS_LINE_SHOT(x1, y1, x2, y2, x0, y0, xS, yS) |
| #define | Y_CROSS_LINE_SHOT(x1, y1, x2, y2, x0, y0, xS, yS) |
| enum | { NODE_INTERIOR, NODE_BOUNDARY, NODE_MARKED } |
| enum | { NODE = 1, EDGE = 2, FACE = 4, LOOP = 8, FREE_FACE = 16 } |
| static PfsSurf * | pfs |
| static int | cur_elemnode |
| static PfsElem * | cur_elem = NULL |
| static PfsElem * | curr_ielem = NULL |
| int | _loop_ = 0 |
| static void | pfs3dGetAreaCoord (double x, double y, double z, double *xn, double *yn, double *zn, double *b0, double *b1, double *b2) |
| static void | pfsParGetAreaCoord (double u, double v, double *un, double *vn, double *b0, double *b1, double *b2) |
| static void | pfsNodeConstrNormal (int ref_id, PfsElem *elem, PFSGeoPoint *normal) |
| static int | pfsAddAdjNode (int ref_id, int adj_id, PfsElem *elem) |
| static int | pfsBuildNodeAdj (void) |
| static int | pfsChkBdryNode (int id) |
| static void | pfsClassifyNodes (void) |
| static int | pfsOrderBdryNodeAdj (int id) |
| static int | pfsOrderAllBdryNodeAdj (void) |
| static void | pfsMarkBdryNodes (void) |
| static void | pfsUnmarkLoopNodes (int ref_id) |
| static void | pfsBuildLoopList (void) |
| static void | pfsDelNodeList (PfsSurf *surf) |
| static void | pfsDelElemList (PfsSurf *surf) |
| static int | pfsGetEdgeAdjElems (int ni, int nj, PfsElem **e_left, PfsElem **e_right) |
| static void | pfsCompute3dBoundBox (void) |
| static void | pfsElemNormal (PfsElem *elem) |
| static void | pfsElemCenter (PfsElem *elem) |
| static void | pfsElemLocalGradients (PfsElem *elem) |
| static void | pfsElem3dBoundBox (PfsElem *elem) |
| static void | pfsNodeNormal (int node) |
| static void | pfsNodeNormals (void) |
| static void | pfsFindRefElem (void) |
| static void | pfsNodeConfMapCoeff (int ref_id) |
| static void | pfsConfMapCoefficients (void) |
| static void | pfsInitParams (void) |
| static int | pfsCreateNextSolOrderLevel (int lev_begin, int lev_end, int *pos, int *solorder, int *nodevisited) |
| static void | pfsBuildSolOrderVec (void) |
| static void | pfsDelSolOrderVec (PfsSurf *surf) |
| static void | pfsSolve2x2 (double a[2][2], double b[2], double *u, double *v) |
| static void | pfsNormalizeParVals (void) |
| static void | pfsComputeParBoundBox (void) |
| static void | pfsElemParBoundBox (PfsElem *elem) |
| static void | pfsComputeElemParBoundBoxes (void) |
| static void | pfsComputeElemJac (PfsElem *elem, double *xdu, double *ydu, double *zdu, double *xdv, double *ydv, double *zdv) |
| static void | pfsNodeJacobian (int node) |
| static void | pfsNodeJacobians (void) |
| static double | pfsArea3d (double xa, double ya, double za, double xb, double yb, double zb, double xc, double yc, double zc, double xn, double yn, double zn) |
| static double | pfsArea2d (double u0, double v0, double u1, double v1, double u2, double v2) |
| static double | pfsDistPntCurElem (PFSGeoPoint *p, PFSGeoPoint *clst) |
| static int | pfsParPntCurElem (double x, double y, double z, double *u, double *v) |
| static int | pfs3dPntCurElem (double u, double v, double *x, double *y, double *z) |
| static int | pfsParDerivCurElem (double u, double v, double *xdu, double *ydu, double *zdu, double *xdv, double *ydv, double *zdv, double *xdw, double *ydw, double *zdw) |
| static int | pfsClstPtParLine (double ua, double va, double ub, double vb, double u, double v, double *up, double *vp, double *dist) |
| static int | pfsIsParPtInside (PFSGeoSurfPar *p) |
| static int | pfsIsParPtOnBound (PFSGeoSurfPar *p) |
| static int | pfsSnapParPtToBound (PFSGeoSurfPar *p) |
| static int | pfsChkProxElemNode (PfsElem *elem, double *u, double *v, int *ni) |
| static int | pfsChkProxElemEdge (PfsElem *elem, double *u, double *v, int *type, int *ni, int *nj) |
| static int | pfsShotXLine (PfsElem *elem, double u0, double v0, double u_shot, double v_shot, int na, int nb, double *u1, double *v1, int *type, int *n_inter) |
| static int | pfsNodeShot (PfsElem *init_elem, double u0, double v0, double u_shot, double v_shot, PfsElem **end_elem, double *u1, double *v1, int *type, int *ni, int *nj) |
| static int | pfsEdgeShot (PfsElem *init_elem, double u0, double v0, double u_shot, double v_shot, PfsElem **end_elem, double *u1, double *v1, int *type, int *ni, int *nj) |
| static int | pfsFaceShot (PfsElem *init_elem, double u0, double v0, double u_shot, double v_shot, PfsElem **end_elem, double *u1, double *v1, int *type, int *ni, int *nj) |
| static int | pfsLoopShot (PfsElem *init_elem, double u0, double v0, double u_shot, double v_shot, PfsElem **end_elem, double *u1, double *v1, int *type, int *ni, int *nj) |
| static int | pfsUpdateShotLen (double u0, double v0, PFSGeoPoint *p0, double *u1, double *v1, PFSGeoPoint *p1, double *len) |
| static void | pfsFinishFreeFaceShotLen (double u0, double v0, PFSGeoPoint *p0, double u_shot, double v_shot, double len, double *u1, double *v1, PFSGeoPoint *p1) |
| static int | pfsShotSolve (PfsElem *init_elem, double u0, double v0, PFSGeoPoint p0, double u_shot, double v_shot, PfsElem **end_elem, double *u1, double *v1, PFSGeoPoint *p1, int *type, int *ni, int *nj, double *len) |
| static int | pfsSolveSurfPar1Pass (void) |
| static int | pfsParPntCurElemAttract (double *x, double *y, double *z, double *u, double *v) |
| void * | pfsRInitSurf (int mxnds, int mxels) |
| void | pfsRActivateSurf (void *surf) |
| void | pfsRFreeSurf (void *surf) |
| int | pfsRAddNode (double x, double y, double z) |
| int | pfsRAddElem (int v0, int v1, int v2) |
| int | pfsRCompleteSurf (void) |
| void | pfsRSolveSurfPar (int maxnumiter) |
| void | pfsCompleteParSpace (void) |
| int | pfsRItr3dBoundBox (double *xmin, double *xmax, double *ymin, double *ymax, double *zmin, double *zmax) |
| int | pfsRItrParBoundBox (double *umin, double *umax, double *vmin, double *vmax) |
| int | pfsRItrFirstElem (void) |
| int | pfsRItrNextElem (void) |
| int | pfsRItrFirst3dElem (double xmin, double xmax, double ymin, double ymax, double zmin, double zmax) |
| int | pfsRItrNext3dElem (double xmin, double xmax, double ymin, double ymax, double zmin, double zmax) |
| int | pfsRItrFirstParElem (double umin, double umax, double vmin, double vmax) |
| int | pfsRItrNextParElem (double umin, double umax, double vmin, double vmax) |
| void | pfsRSetCurrElem (void *elem) |
| int | pfsRGetElem (double x, double y, double z, void **elem) |
| int | pfsRGetLoopElem (double x, double y, double z, void **elem) |
| int | pfsRItrElemNode (int *id) |
| void | pfsRItrElemCenter (double *x, double *y, double *z) |
| void | pfsRItrElemNormal (double *nx, double *ny, double *nz) |
| void | pfsRItrElem3dBox (double *xmin, double *ymin, double *zmin, double *xmax, double *ymax, double *zmax) |
| void | pfsRItrElemParBox (double *umin, double *vmin, double *umax, double *vmax) |
| int | pfsRItrNumNodes (void) |
| void | pfsRItrNodeCoords (int id, double *x, double *y, double *z) |
| void | pfsRItrNodeNormal (int id, double *nx, double *ny, double *nz) |
| void | pfsRItrNodeJacobian (int id, double *xdu, double *ydu, double *zdu, double *xdv, double *ydv, double *zdv) |
| void | pfsRItrNodeParVals (int id, double *u, double *v) |
| int | pfsRItrNumLoops (void) |
| int | pfsRItrFirstLoopNode (int loop_id, int *id) |
| int | pfsRItrNextLoopNode (int loop_id, int ref_id, int *id) |
| int | pfsRProjectOn (double x, double y, double z, double *u, double *v) |
| int | pfsSnapToBound (double *u, double *v, double toler) |
| int | pfsRGetJacobian (double u, double v, double *xdu, double *ydu, double *zdu, double *xdv, double *ydv, double *zdv, double *xdw, double *ydw, double *zdw) |
| int | pfsREval (double u, double v, double *x, double *y, double *z) |
| int | pfsRShot (void *init_elem, double x0, double y0, double z0, double u_shot, double v_shot, double len, void **end_elem, double *x1, double *y1, double *z1) |
| #define COL_TOLER 1e-5 |
Definition at line 170 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by pfsChkProxElemEdge(), pfsChkProxElemNode(), pfsParPntCurElem(), and pfsParPntCurElemAttract().
| #define DET2D | ( | a, | |||
| b, | |||||
| c, | |||||
| d | ) | (((a)*(d))-((b)*(c))) |
| #define ITER_TOLER 0.0001 |
| #define Len2 | ( | x, | |||
| y | ) | sqrt((double)(((x)*(x))+((y)*(y)))) |
| #define Len3 | ( | x, | |||
| y, | |||||
| z | ) | sqrt((double)(((x)*(x))+((y)*(y))+((z)*(z)))) |
| #define TOLER 1e-5 |
Definition at line 168 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by pfs3dPntCurElem(), pfsChkProxElemEdge(), pfsIsParPtInside(), pfsIsParPtOnBound(), pfsParDerivCurElem(), pfsRProjectOn(), pfsRShot(), and pfsUpdateShotLen().
| #define X_CROSS_LINE_LINE | ( | x1, | |||
| y1, | |||||
| x2, | |||||
| y2, | |||||
| x3, | |||||
| y3, | |||||
| x4, | |||||
| y4 | ) |
| #define X_CROSS_LINE_SHOT | ( | x1, | |||
| y1, | |||||
| x2, | |||||
| y2, | |||||
| x0, | |||||
| y0, | |||||
| xS, | |||||
| yS | ) |
Value:
Intersection line-shot obtained substituting second line by a point and a vector direction.Definition at line 205 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by pfsClstPtParLine(), and pfsShotXLine().
| #define Y_CROSS_LINE_LINE | ( | x1, | |||
| y1, | |||||
| x2, | |||||
| y2, | |||||
| x3, | |||||
| y3, | |||||
| x4, | |||||
| y4 | ) |
| #define Y_CROSS_LINE_SHOT | ( | x1, | |||
| y1, | |||||
| x2, | |||||
| y2, | |||||
| x0, | |||||
| y0, | |||||
| xS, | |||||
| yS | ) |
| anonymous enum |
| static void pfs3dGetAreaCoord | ( | double | x, | |
| double | y, | |||
| double | z, | |||
| double * | xn, | |||
| double * | yn, | |||
| double * | zn, | |||
| double * | b0, | |||
| double * | b1, | |||
| double * | b2 | |||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 461 of file pfs.c.
References PfsElem::normal, pfsArea3d(), PFSGeoPoint::x, PFSGeoPoint::y, and PFSGeoPoint::z.
Referenced by pfsParPntCurElem(), and pfsParPntCurElemAttract().
| static int pfs3dPntCurElem | ( | double | u, | |
| double | v, | |||
| double * | x, | |||
| double * | y, | |||
| double * | z | |||
| ) | [static] |
Given the parametric space of a point that is presumably in the current element, this function returns the cartesian coordinates of that point. If the given point is not inside the current element, it returns a false (0) status. Otherwise, it returns a true (1) status. In any case, it computes the cartesian coordinates of the given point assuming that it is inside the given element, i.e, using natural triangular (baricentric) interpolation of element nodes cartesian coordinates. It is assumed that there is a defined current element.
Definition at line 2521 of file pfs.c.
References PfsElem::inc, pfsParGetAreaCoord(), pfsRItrNodeCoords(), pfsRItrNodeParVals(), and TOLER.
Referenced by pfsFinishFreeFaceShotLen(), pfsLoopShot(), pfsREval(), pfsRShot(), pfsShotSolve(), and pfsUpdateShotLen().
| static int pfsAddAdjNode | ( | int | ref_id, | |
| int | adj_id, | |||
| PfsElem * | elem | |||
| ) | [static] |
int pfsAddAdjNode( int ref_id, int adj_id, PfsElem* elem )
ref_id - id of reference node (in) adj_id - id of adjacent node (in) elem - counter-clockwise adjacent element (in) when looking from reference to adjacent node (or elem = null, if adjancent element is clockwise with respect to this node-node relationship)
This function checks to see if an adjacent node (given by its id) is already in the linked list of adjacent nodes of a reference node (given by its id). If the adjacent node is already in the list, the function does the following:
Definition at line 606 of file pfs.c.
References PfsNode::adj_head, PfsAdjNode::AtA, PfsNode::coord, PFSGeoLine::d, PfsNode::degree, PFSGeoLine::e, PfsAdjNode::elem, PfsAdjNode::id, PfsAdjNode::next, PfsSurf::nodelist, PFS_INVERSE_INCIDENCE, PFS_NON_MANIFOLD_EDGE, PFS_SUCCESS, PFSGeoAngPtAboutLine(), pfsNodeConstrNormal(), and PfsAdjNode::refcnt.
Referenced by pfsBuildNodeAdj().

| static double pfsArea2d | ( | double | u0, | |
| double | v0, | |||
| double | u1, | |||
| double | v1, | |||
| double | u2, | |||
| double | v2 | |||
| ) | [static] |
This function computes the area of a triangle in parametric space.
Definition at line 2295 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by pfsParGetAreaCoord().
| static double pfsArea3d | ( | double | xa, | |
| double | ya, | |||
| double | za, | |||
| double | xb, | |||
| double | yb, | |||
| double | zb, | |||
| double | xc, | |||
| double | yc, | |||
| double | zc, | |||
| double | xn, | |||
| double | yn, | |||
| double | zn | |||
| ) | [static] |
This function computes the area of a triangle in cartesian space.
Definition at line 2262 of file pfs.c.
References PFSGeoCrossProd(), PFSGeoDotProd(), PFSGeoVecLen(), PFSGeoPoint::x, PFSGeoPoint::y, and PFSGeoPoint::z.
Referenced by pfs3dGetAreaCoord().
| static void pfsBuildLoopList | ( | void | ) | [static] |
This function creates a list vector with the first node of each loop (connected boundary portion) of current surface. It allocates a temporary vector for the loop list with size equals to the number of nodes. It uses this vector to store the first node of each loop as it builds the list and computes the number of loops. At the end it allocates the final list vector with the correct size. The algorithm does the following: (a) First it marks all the boundary nodes. (b) Then it goes to the first found marked boundary node and counts a new loop. (c) Then it tranverses the boundary loop that starts at the found marked node and unmarks all the visited boundary nodes. (d) It goes back to step (b) until there are marked boundary nodes.
Definition at line 1036 of file pfs.c.
References PfsSurf::looplist, NODE_MARKED, PfsSurf::nodelist, PfsSurf::numelems, PfsSurf::numloops, PfsSurf::numnodes, pfsMarkBdryNodes(), pfsUnmarkLoopNodes(), and PfsNode::type.
Referenced by pfsRCompleteSurf().
| static int pfsBuildNodeAdj | ( | void | ) | [static] |
This function builds the node-node adjacency relationships and stores them in the data base. It creates the linked lists of adjacent nodes for each node in the mesh. These lists are hanged on each node of the node list vector. Two nodes are considered adjacent when they form a boundary segment of an element. The algorithm used to create these linked lists is the following:
Definition at line 756 of file pfs.c.
References PfsSurf::elm3d_tree, PfsElem::inc, PFS_SUCCESS, pfsAddAdjNode(), PFSRtreeInitTraverse(), and PFSRtreeTraverse().
Referenced by pfsRCompleteSurf().
| static void pfsBuildSolOrderVec | ( | void | ) | [static] |
This function allocates and builds the node solution order vector. If there is already a node solution vector allocated, this function releases the memory used by this vector. It allocates a vector that will contain indices of the nodes of the current active surface in the order that they will be processed in the iterative solution to obtain nodal parametric coordinates. The first index of the vector is initialized as the index of the reference node (the origin of parametric space). To fill all the remaining indices in the vector an algorithm based on the node-adjacency structure is used. For this algorithm, an auxiliary vector that stores a flag for each node already visited is created. The first flag (corresponding to the reference node) is set as true (1) and the remaining flags are inicialized as false (0). The nodes are visited and inserted in the solution order vector by levels of adjacency. Each level is created with the nodes that are adjacent to the nodes of the previous level and that have not been visited. The first level contains the reference node. The iteration terminates when all the nodes adjacent to the nodes of the current level have already been visited.
Definition at line 1879 of file pfs.c.
References PfsSurf::numnodes, pfsCreateNextSolOrderLevel(), pfsDelSolOrderVec(), pos, PfsSurf::ref_node, and PfsSurf::sol_order.
Referenced by pfsRCompleteSurf().
| static int pfsChkBdryNode | ( | int | id | ) | [static] |
Given an index of a node, this function checks to see that the node is on the boundary of the surface mesh. The algorithm used to check for boundary node is the following: Traverse the linked list of adjacent nodes of the given node looking for an node-node adjacency relationship with a reference counter different than 2 (which indicates a border edge). If this is found, the function returns a valid (1) status. Otherwise, it returns a false (0) status.
Definition at line 821 of file pfs.c.
References PfsNode::adj_head, PfsAdjNode::next, PfsSurf::nodelist, and PfsAdjNode::refcnt.
Referenced by pfsClassifyNodes().

| static int pfsChkProxElemEdge | ( | PfsElem * | elem, | |
| double * | u, | |||
| double * | v, | |||
| int * | type, | |||
| int * | ni, | |||
| int * | nj | |||
| ) | [static] |
Dados um elemento e as coordenadas paramétricas de um ponto, verifica se o ponto coincide com algum dos nós ou arestas do elemento dado, considerando essa precedência e um certa tolerância. Quando verificada a proximidade, o pto é atraído para a posição do nó ou para a posição da projeção do pto sobre a aresta, retornando o índice do nó ou dos nós da aresta, e o tipo da entidade para a qual o pto foi atraído (NODE ou EDGE).
| elem | - elemento q a busca será feita (in) | |
| u,v | - coordenadas paramétricas do ponto (in/out) | |
| type | - tipo da entidade para a qual o pto foi atraído (out) | |
| ni,nj | - índice do nó ou nós da aresta (out) |
Definition at line 2987 of file pfs.c.
References COL_TOLER, EDGE, PfsElem::inc, NODE, pfsParGetAreaCoord(), pfsRItrNodeParVals(), and TOLER.
Referenced by pfsRShot().


| static int pfsChkProxElemNode | ( | PfsElem * | elem, | |
| double * | u, | |||
| double * | v, | |||
| int * | ni | |||
| ) | [static] |
Dados um elemento e as coordenadas paramétricas de um ponto, verifica se o ponto coincide com algum dos nós do elemento dado, considerando uma certa tolerância. Quando verificada a proximidade, o pto é atraído para a posição do nó, retornando o índice do nó.
| elem | - elemento q a busca será feita (in) | |
| u,v | - coordenadas paramétricas do ponto (in/out) | |
| ni | - índice do nó (out) |
Definition at line 2933 of file pfs.c.
References COL_TOLER, PfsElem::inc, pfsParGetAreaCoord(), and pfsRItrNodeParVals().
Referenced by pfsShotXLine().

| static void pfsClassifyNodes | ( | void | ) | [static] |
This function classifies all nodes of current surface as either interior or boundary.
Definition at line 842 of file pfs.c.
References NODE_BOUNDARY, NODE_INTERIOR, PfsSurf::nodelist, PfsSurf::numnodes, pfsChkBdryNode(), and PfsNode::type.
Referenced by pfsRCompleteSurf().
| static int pfsClstPtParLine | ( | double | ua, | |
| double | va, | |||
| double | ub, | |||
| double | vb, | |||
| double | u, | |||
| double | v, | |||
| double * | up, | |||
| double * | vp, | |||
| double * | dist | |||
| ) | [static] |
This function computes the 2D (parametric) coordinates of the closest point of a given parametric point on a line (ab).
| ua,va,ub,vb | - parametric coordinates of line pts. (in) | |
| u,v | - param. coords. of given pt. (in) | |
| up,vp | - param. coordinates of closest pt. (out) | |
| dist | - param. distance from pt. to clst.pt. (out) |
Definition at line 2640 of file pfs.c.
References Len2, size, X_CROSS_LINE_SHOT, and Y_CROSS_LINE_SHOT.
Referenced by pfsIsParPtOnBound(), and pfsSnapParPtToBound().
| void pfsCompleteParSpace | ( | void | ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
void pfsCompleteParSpace( void )
This function finishes up definition of surface parametric values of all nodes of the mesh in current active surface. First it normalizes the parametric coordinates of all nodes of surface. The normalization is such that the minimum parametric value is zero and the maximum is one. In the normalization, the same scaling factor is applyed to both u and v parametric coordinates. Then, it computes the bounding box parametric components for each element in the current mesh and creates the R-tree of elements indexed by parametric bounding box. Finally, it computes an average Jacobian (mapping derivatives) for each node in the current mesh. Each node jacobian is computed as an average of the Jacobians of the adjacent elements.
Definition at line 4086 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by ConstSurfaceBuild().

| static void pfsCompute3dBoundBox | ( | void | ) | [static] |
This function computes the 3D bounding box of the current mesh.
Definition at line 1199 of file pfs.c.
References PfsSurf::box_xmax, PfsSurf::box_xmin, PfsSurf::box_ymax, PfsSurf::box_ymin, PfsSurf::box_zmax, PfsSurf::box_zmin, PfsNode::coord, PfsSurf::nodelist, PfsSurf::numnodes, PFSGeoPoint::x, PFSGeoPoint::y, and PFSGeoPoint::z.
Referenced by pfsRCompleteSurf().
| static void pfsComputeElemJac | ( | PfsElem * | elem, | |
| double * | xdu, | |||
| double * | ydu, | |||
| double * | zdu, | |||
| double * | xdv, | |||
| double * | ydv, | |||
| double * | zdv | |||
| ) | [static] |
This function computes jacobian components of a given element.
Definition at line 2146 of file pfs.c.
References PfsNode::coord, PfsElem::inc, PfsSurf::nodelist, PfsNode::par, PFSGeoSurfPar::u, PFSGeoSurfPar::v, PFSGeoPoint::x, PFSGeoPoint::y, and PFSGeoPoint::z.
Referenced by pfsNodeJacobian().

| static void pfsComputeElemParBoundBoxes | ( | void | ) | [static] |
This function computes the bounding box parametric components for each element in the current mesh and creates the R-tree of elements indexed by parametric bounding box.
Definition at line 2120 of file pfs.c.
References PfsSurf::elm3d_tree, pfsElemParBoundBox(), PFSRtreeInitTraverse(), and PFSRtreeTraverse().
Referenced by pfsCompleteParSpace().

| static void pfsComputeParBoundBox | ( | void | ) | [static] |
This function computes the parametric bounding box of the current mesh.
Definition at line 2050 of file pfs.c.
References PfsSurf::box_umax, PfsSurf::box_umin, PfsSurf::box_vmax, PfsSurf::box_vmin, PfsSurf::nodelist, PfsSurf::numnodes, PfsNode::par, PFSGeoSurfPar::u, and PFSGeoSurfPar::v.
Referenced by pfsRCompleteSurf(), and pfsRSolveSurfPar().
| static void pfsConfMapCoefficients | ( | void | ) | [static] |
void pfsConfMapCoefficients( void )
This function compute the conformal map coefficients of all the nodes of the surface.
Definition at line 1713 of file pfs.c.
References PfsSurf::nodelist, PfsSurf::numnodes, pfsNodeConfMapCoeff(), and PfsSurf::ref_elem.
Referenced by pfsRCompleteSurf().

| static int pfsCreateNextSolOrderLevel | ( | int | lev_begin, | |
| int | lev_end, | |||
| int * | pos, | |||
| int * | solorder, | |||
| int * | nodevisited | |||
| ) | [static] |
int pfsCreateNextSolOrderLevel( int lev_begin, int lev_end, int *pos, int *solorder, int *nodevisited )
lev_begin - id of first node of current level in solorder (in) lev_end - id of last node of current level in solorder (in) pos - index of current node in solorder vector (in/out) solorder - vector of node solution order (in) nodevisited - vector of flags for nodes already visited (in)
This function inserts the next level of nodes in the solution order vector. It traverses the linked list of adjacent nodes of each node of the current level and adds non-visited adjacent node to the solution order vector. The function returns a true (1) value if there is at least one node adjacent to one of the nodes of the current level that has not been visited, i.e., that has not been added to the solution order vector. Otherwise, it returns a false (0) value.
Definition at line 1826 of file pfs.c.
References PfsNode::adj_head, PfsAdjNode::id, PfsAdjNode::next, and PfsSurf::nodelist.
Referenced by pfsBuildSolOrderVec().

| static void pfsDelElemList | ( | PfsSurf * | surf | ) | [static] |
This function releases memory of element cartesian and parametric Rtrees, and of list vector of incidence nodes of each element.
Definition at line 1116 of file pfs.c.
References PfsSurf::elm2d_tree, PfsSurf::elm3d_tree, PFSRtreeDestroy(), PFSRtreeInitTraverse(), and PFSRtreeTraverse().
Referenced by pfsRFreeSurf().
| static void pfsDelNodeList | ( | PfsSurf * | surf | ) | [static] |
This function releases memory of node list vector and linked lists of adjancent nodes of each node.
Definition at line 1090 of file pfs.c.
References PfsNode::adj_head, PfsAdjNode::next, PfsSurf::nodelist, and PfsSurf::numnodes.
Referenced by pfsRFreeSurf().
| static void pfsDelSolOrderVec | ( | PfsSurf * | surf | ) | [static] |
This function deallocates the memory used for the node solution order vector and reset the pointer to it.
Definition at line 1916 of file pfs.c.
References PfsSurf::sol_order.
Referenced by pfsBuildSolOrderVec(), and pfsRFreeSurf().

| static double pfsDistPntCurElem | ( | PFSGeoPoint * | p, | |
| PFSGeoPoint * | clst | |||
| ) | [static] |
This function returns in its value the minimum distance between a given point (p) and the plane that contains current traversed triangular element. It also returns the cartesian coordinates of the closest point on the element plane. It does not check to see whether the closest point on plane is inside current element. It is assumed that there is a defined current element.
Definition at line 2320 of file pfs.c.
References PFSGeoNormPlane::a, PfsElem::inc, PFSGeoNormPlane::n, PfsElem::normal, PFSGeoClstPtNormPlane(), PFSGeoCrossProd(), PFSGeoDiffVec(), PFSGeoDist(), PFSGeoVecNormalize(), pfsRItrNodeCoords(), PFSGeoNormPlane::u, PFSGeoNormPlane::v, PFSGeoPoint::x, PFSGeoPoint::y, and PFSGeoPoint::z.
Referenced by pfsRProjectOn().
| static int pfsEdgeShot | ( | PfsElem * | init_elem, | |
| double | u0, | |||
| double | v0, | |||
| double | u_shot, | |||
| double | v_shot, | |||
| PfsElem ** | end_elem, | |||
| double * | u1, | |||
| double * | v1, | |||
| int * | type, | |||
| int * | ni, | |||
| int * | nj | |||
| ) | [static] |
Esta função calcula a interseção de um tiro, que parte de um pto localizado sobre uma aresta, com os nos e arestas dos elementos adjacentes `a aresta. Retorna o tipo de intersecao (NODE ou EDGE), o(s) indice(s) do(s) nó(s) correspondente(s) e o elemento que contem o nó ou aresta. Caso o elemento inicial seja nulo, todos os testes são feitos para os dois triangulos adjacentes a aresta, pois não se sabe a princípio de qual triangulo está vindo o tiro. Caso contrario, significa que o tiro está vindo do elemento inicial, logo ele não precisa ser testado. Se o tiro nao intercepta nenhum nó ou aresta, o elemento retornado é o elemento inicial e o tipo de entrada ganha um status de fronteira (LOOP).
Definition at line 3292 of file pfs.c.
References EDGE, PfsElem::inc, LOOP, NODE, pfs_node, pfsGetEdgeAdjElems(), and pfsShotXLine().
Referenced by pfsShotSolve().

| static void pfsElem3dBoundBox | ( | PfsElem * | elem | ) | [static] |
This function computes the components of 3D bounding box of the given element and inserts the element in R-tree indexed by 3D bounding boxes.
Definition at line 1383 of file pfs.c.
References PfsNode::coord, PfsSurf::elm3d_tree, PfsElem::inc, PfsElem::max3dbox, PfsElem::min3dbox, PfsSurf::nodelist, PFSRtreeInsert(), PFSGeoPoint::x, PFSGeoPoint::y, and PFSGeoPoint::z.
Referenced by pfsRAddElem().
| static void pfsElemCenter | ( | PfsElem * | elem | ) | [static] |
This function computes the center point of an element (given by its id). The center point is computed based on an average of the coordinates of the element nodes.
Definition at line 1286 of file pfs.c.
References PfsElem::center, PfsNode::coord, PfsElem::inc, PfsSurf::nodelist, PFSGeoPoint::x, PFSGeoPoint::y, and PFSGeoPoint::z.
Referenced by pfsRAddElem().
| static void pfsElemLocalGradients | ( | PfsElem * | elem | ) | [static] |
Find local planar coordinates for the triangle vertices. Considering that r2 is the distance between v0 and v1, assume that v0 is at local (0,0), v1 is at (r2,0), and the coordinates of v2 are found from the simultanious solution of two circle equations (done by Wash). See section 2.4 of Levy, Petitjean, Ray, and Maillot, "Least squares conformal maps for automatic texture atlas generation," SIGRAPH proceedings, 2002.
Definition at line 1319 of file pfs.c.
References PfsNode::coord, PfsElem::inc, Len3, PfsSurf::nodelist, PfsElem::W, PFSGeoPoint::x, PFSGeoPoint::y, and PFSGeoPoint::z.
Referenced by pfsRAddElem().
| static void pfsElemNormal | ( | PfsElem * | elem | ) | [static] |
This function computes an average normal vector of an element (given by its id). The normal vector is computed adding up cross products between the first element edge and the other edges. The modulus of the cross-product vector is twice the area of the triangle. The area of each triangle is also stored in the corresponding field of the given element.
Definition at line 1236 of file pfs.c.
References PfsElem::area, PfsNode::coord, PfsElem::inc, PfsSurf::nodelist, PfsElem::normal, PFSGeoVecLen(), size, PFSGeoPoint::x, PFSGeoPoint::y, and PFSGeoPoint::z.
Referenced by pfsRAddElem().
| static void pfsElemParBoundBox | ( | PfsElem * | elem | ) | [static] |
This function computes the components of parametric bounding box of the given element and inserts the element in R-tree indexed by parametric bounding boxes.
Definition at line 2079 of file pfs.c.
References PfsSurf::elm2d_tree, PfsElem::inc, PfsElem::maxparbox, PfsElem::minparbox, PfsSurf::nodelist, PfsNode::par, PFSRtreeInsert(), PFSGeoSurfPar::u, and PFSGeoSurfPar::v.
Referenced by pfsComputeElemParBoundBoxes().
| static int pfsFaceShot | ( | PfsElem * | init_elem, | |
| double | u0, | |||
| double | v0, | |||
| double | u_shot, | |||
| double | v_shot, | |||
| PfsElem ** | end_elem, | |||
| double * | u1, | |||
| double * | v1, | |||
| int * | type, | |||
| int * | ni, | |||
| int * | nj | |||
| ) | [static] |
Esta função calcula a interseção de um tiro, que parte de um pto localizado em um elemento (face), com os nos e arestas do elemento. Retorna o tipo de intersecao (NODE ou EDGE) e o(s) indice(s) do(s) nó(s) correspondente(s). O elemento final retornado é o próprio elemento inicial.
Definition at line 3407 of file pfs.c.
References EDGE, PfsElem::inc, NODE, pfs_node, and pfsShotXLine().
Referenced by pfsShotSolve().

| static void pfsFindRefElem | ( | void | ) | [static] |
This function finds the element that will contain the origin of the parametric coordinate space. First it computes a global average normal vector from the normal vectors of all elements of the surface. This is a weighted average considering the area as the weight of each element. Then it searchs for an element that has an area greater the avarage area values of all elements and that has the greatest dot product value computed from its normal vector and the average normal vector. This element will be the reference element that contains the origin of the parametric space. The origin is the first node of the element. This function also defines the tolerance used to terminate the iterative solution of nodal parametric values: the tolerance is defined as a factor of the size of first reference element side (from the reference node to the next element node in counter-clockwise order).
Definition at line 1505 of file pfs.c.
References PfsElem::area, PfsNode::coord, PfsSurf::elm3d_tree, PfsElem::inc, ITER_TOLER, PfsSurf::iter_toler, Len3, PfsSurf::nodelist, PfsElem::normal, PfsSurf::numelems, PFSGeoDotProd(), PFSGeoVecLen(), PFSRtreeInitTraverse(), PFSRtreeTraverse(), PfsSurf::ref_elem, PfsSurf::ref_node, size, PFSGeoPoint::x, PFSGeoPoint::y, and PFSGeoPoint::z.
Referenced by pfsRCompleteSurf().
| static void pfsFinishFreeFaceShotLen | ( | double | u0, | |
| double | v0, | |||
| PFSGeoPoint * | p0, | |||
| double | u_shot, | |||
| double | v_shot, | |||
| double | len, | |||
| double * | u1, | |||
| double * | v1, | |||
| PFSGeoPoint * | p1 | |||
| ) | [static] |
Esta função finaliza o caminhamento a ser percorrido ao longo do último segmento da semi-linha de tiro no espaço paramétrico na área externa à superfície (FREE_FACE). A função calcula o ponto no segmento da linha de tiro, que parte do ponto inicial no espaço paramétrico (u0,v0) com direção no espaço paramétrico dada por (u_shot,v_shot), que tem uma distância ao ponto inicial igual ao comprimento dado.
| u0,v0 | (in) posição inicial do tiro no espaço paramétrico | |
| p0 | (in) posição inicial do tiro no espaço cartesiano | |
| u_shot,v_shot | (in) direção do tiro no espaço paramétrico | |
| len | (in) comprimento do caminho que deve ser percorrido no espaço | |
| u1,v1 | (in/out) posição final do tiro no espaço paramétrico | |
| p1 | (in/out) posição final do tiro no espaço cartesiano |
Definition at line 3686 of file pfs.c.
References pfs3dPntCurElem(), PFSGeoDiffVec(), PFSGeoProdScalVec(), PFSGeoSumVec(), PFSGeoVecNormalize(), pfsParPntCurElemAttract(), PFSGeoPoint::x, PFSGeoPoint::y, and PFSGeoPoint::z.
Referenced by pfsShotSolve().

This function gets the two adjacente elements of a pair of adjacent nodes.
| ni | - first node of edge (in) | |
| nj | - second node of edge (in) | |
| e_left | - element to the left as seem from ni to nj (out) | |
| e_right | - element to the right as seem from ni to nj (out) |
Definition at line 1157 of file pfs.c.
References PfsNode::adj_head, PfsAdjNode::elem, PfsAdjNode::id, PfsAdjNode::next, and PfsSurf::nodelist.
Referenced by pfsEdgeShot().

| static void pfsInitParams | ( | void | ) | [static] |
This function initializes the parametric values of all nodes of the active surface mesh. The initial parametric values are computed based on the projection of each mesh node onto the plane that contains reference element. The result is that the first node of the reference element (the reference node) will have parametric coordinates equal to (u,v) = (0,0), which will never be changed. The function tries to lay the first plane parametric vector be at the projection of the major x-axis with the plane. If the x-axis is almost (less then 30 degrees) parallel to the plane normal vector, it tries to do the same with the y-axis and z-axis (in this order).
Definition at line 1744 of file pfs.c.
References PFSGeoNormPlane::a, ABS, PfsNode::coord, PFSGeoNormPlane::n, PfsSurf::nodelist, PfsElem::normal, PfsSurf::numnodes, PfsNode::par, PFSGeoClstPtNormPlane(), PFSGeoCrossProd(), PFSGeoVecLen(), PFSGeoVecNormalize(), PfsSurf::ref_elem, PfsSurf::ref_node, PFSGeoSurfPar::u, PFSGeoNormPlane::u, PFSGeoSurfPar::v, PFSGeoNormPlane::v, PFSGeoPoint::x, PFSGeoPoint::y, and PFSGeoPoint::z.
Referenced by pfsRCompleteSurf().
| static int pfsIsParPtInside | ( | PFSGeoSurfPar * | p | ) | [static] |
This function checks whether the given point in parametric coordinates is inside the surface model.
Definition at line 2702 of file pfs.c.
References PFS_SUCCESS, pfsRItrFirstLoopNode(), pfsRItrNextLoopNode(), pfsRItrNodeParVals(), pfsRItrNumLoops(), TOLER, PFSGeoSurfPar::u, and PFSGeoSurfPar::v.
Referenced by pfsREval(), and pfsRGetJacobian().
| static int pfsIsParPtOnBound | ( | PFSGeoSurfPar * | p | ) | [static] |
This function checks whether the given point in parametric coordinates is on the boundary of the surface model.
Definition at line 2797 of file pfs.c.
References PFS_SUCCESS, pfsClstPtParLine(), pfsRItrFirstLoopNode(), pfsRItrNextLoopNode(), pfsRItrNodeParVals(), pfsRItrNumLoops(), TOLER, PFSGeoSurfPar::u, and PFSGeoSurfPar::v.
Referenced by pfsREval(), and pfsRGetJacobian().
| static int pfsLoopShot | ( | PfsElem * | init_elem, | |
| double | u0, | |||
| double | v0, | |||
| double | u_shot, | |||
| double | v_shot, | |||
| PfsElem ** | end_elem, | |||
| double * | u1, | |||
| double * | v1, | |||
| int * | type, | |||
| int * | ni, | |||
| int * | nj | |||
| ) | [static] |
Esta função calcula a interseção de um tiro com os nos e arestas que formam uma fronteira. Como podem ocorrer várias interseções, o pto retornado é o pto mais próximo ao pto inicial do tiro. Quando o tiro parte de um pto sobre um nó, não verifica-se a interseção do tiro com as arestas do loop adjacentes ao nó. Qdo parte de uma aresta, não verifica-se a interseção do tiro, com a aresta sobre a qual está o pto. Qdo o pto está na face externa, verifica-se a interseção com todas as arestas do loop.
Definition at line 3456 of file pfs.c.
References PfsNode::adj_head, EDGE, FREE_FACE, NODE, NODE_BOUNDARY, PfsSurf::nodelist, PfsSurf::numelems, PfsSurf::numloops, PfsSurf::numnodes, pfs3dPntCurElem(), PFSGeoDist(), pfsRItrNodeCoords(), pfsRSetCurrElem(), pfsShotXLine(), PfsNode::type, PFSGeoPoint::x, PFSGeoPoint::y, and PFSGeoPoint::z.
Referenced by pfsShotSolve().

| static void pfsMarkBdryNodes | ( | void | ) | [static] |
This function marks all boundary nodes. It traverses the list of nodes and for each boundary node sets its type as NODE_MARKED.
Definition at line 971 of file pfs.c.
References NODE_BOUNDARY, NODE_MARKED, PfsSurf::nodelist, PfsSurf::numnodes, and PfsNode::type.
Referenced by pfsBuildLoopList().

| static void pfsNodeConfMapCoeff | ( | int | ref_id | ) | [static] |
void pfsNodeConfMapCoeff( int ref_id )
ref_id - id of reference node (in)
This function computes the conformal map coefficients that are related to a given node (given by its id). See section 2.4 of Levy, Petitjean, Ray, and Maillot, "Least squares conformal maps for automatic texture atlas generation," SIGRAPH proceedings, 2002.
Definition at line 1595 of file pfs.c.
References PfsNode::adj_head, PfsAdjNode::AtA, PfsNode::AtA, PfsAdjNode::elem, PfsAdjNode::id, PfsElem::inc, PfsAdjNode::next, PfsSurf::nodelist, and PfsElem::W.
Referenced by pfsConfMapCoefficients().
| static void pfsNodeConstrNormal | ( | int | ref_id, | |
| PfsElem * | elem, | |||
| PFSGeoPoint * | normal | |||
| ) | [static] |
void pfsNodeConstrNormal( int ref_id, PfsElem *elem, PFSGeoPoint *normal )
ref_id - id of reference node (in) elem - counter-clockwise adjacent element (in) when looking from reference to adjacent node (or elem = null, if adjancent element is clockwise with respect to this node-node relationship) normal - returned construction normal vector.
This function computes an average normal vector of a node (given by its index) and the given element normal. The normal vector is computed as an average of the normal vectors of the node adjacent elements. If the given "elem" pointer is null, it is simply not considered in the average normal vector. The computed normal vector is only returned, i.e., it is not stored in the corresponding field of the target node structure.
Definition at line 514 of file pfs.c.
References PfsNode::adj_head, PfsAdjNode::elem, PfsAdjNode::next, PfsSurf::nodelist, PfsElem::normal, PFSGeoVecLen(), size, PFSGeoPoint::x, PFSGeoPoint::y, and PFSGeoPoint::z.
Referenced by pfsAddAdjNode().

| static void pfsNodeJacobian | ( | int | id | ) | [static] |
This function computes an average nodal jacobian of a node (given by its id). The nodal jacobian is computed as an average of the nodal jacobians of the node adjacent elements.
Definition at line 2189 of file pfs.c.
References PfsNode::adj_head, PfsNode::ddu, PfsNode::ddv, PfsAdjNode::elem, PfsAdjNode::next, PfsSurf::nodelist, pfsComputeElemJac(), PFSGeoPoint::x, PFSGeoPoint::y, and PFSGeoPoint::z.
Referenced by pfsNodeJacobians().
| static void pfsNodeJacobians | ( | void | ) | [static] |
This function computes an average nodal jacobian for each node in the current mesh. Each node jacobian is computed as an average of the jacobians of the adjacent elements.
Definition at line 2245 of file pfs.c.
References PfsSurf::nodelist, PfsSurf::numnodes, and pfsNodeJacobian().
Referenced by pfsCompleteParSpace().

| static void pfsNodeNormal | ( | int | id | ) | [static] |
This function computes an average normal vector of a node (given by its id). The normal vector is computed as an average of the normal vectors of the node adjacent elements.
Definition at line 1434 of file pfs.c.
References PfsNode::adj_head, PfsAdjNode::elem, PfsAdjNode::next, PfsSurf::nodelist, PfsElem::normal, PfsNode::normal, PFSGeoVecLen(), size, PFSGeoPoint::x, PFSGeoPoint::y, and PFSGeoPoint::z.
Referenced by pfsNodeNormals().

| static void pfsNodeNormals | ( | void | ) | [static] |
This function computes an average normal vector for each node in the current mesh. Each node normal is computed as an average of the normals of the adjacent elements.
Definition at line 1473 of file pfs.c.
References PfsSurf::nodelist, PfsSurf::numnodes, and pfsNodeNormal().
Referenced by pfsRCompleteSurf().

| static int pfsNodeShot | ( | PfsElem * | init_elem, | |
| double | u0, | |||
| double | v0, | |||
| double | u_shot, | |||
| double | v_shot, | |||
| PfsElem ** | end_elem, | |||
| double * | u1, | |||
| double * | v1, | |||
| int * | type, | |||
| int * | ni, | |||
| int * | nj | |||
| ) | [static] |
Esta função calcula a interseção de um tiro, que parte de um pto localizado em um nó, com os nos e arestas dos elementos adjacentes ao nó. Retorna o tipo de intersecao (NODE ou EDGE), o(s) indice(s) do(s) nó(s) correspondente(s) e o elemento que contem o nó ou aresta. Caso o elemento inicial seja nulo, todos os testes são feitos para todos os triangulos adjacentes ao no', pois não se sabe a princípio de qual triangulo está vindo o tiro. Caso contrario, significa que o tiro está vindo do elemento inicial, logo ele não precisa ser testado. Se o tiro nao intercepta nenhum nó ou aresta, o elemento retornado é o elemento inicial e o tipo de entrada ganha um status de fronteira (LOOP).
Definition at line 3198 of file pfs.c.
References PfsNode::adj_head, EDGE, PfsAdjNode::elem, PfsAdjNode::id, PfsElem::inc, LOOP, PfsAdjNode::next, NODE, PfsSurf::nodelist, pfs_node, and pfsShotXLine().
Referenced by pfsShotSolve().

| static void pfsNormalizeParVals | ( | void | ) | [static] |
This function normalizes the parametric coordinates of all nodes of surface. The normalization is such that the minimum parametric value is zero and the maximum is one. In the normalization, the same scaling factor is applyed to both u and v parametric coordinates.
Definition at line 2013 of file pfs.c.
References PfsSurf::box_umax, PfsSurf::box_umin, PfsSurf::box_vmax, PfsSurf::box_vmin, MAX, PfsSurf::nodelist, PfsSurf::numnodes, PfsNode::par, PFSGeoSurfPar::u, and PFSGeoSurfPar::v.
Referenced by pfsCompleteParSpace().
| static int pfsOrderAllBdryNodeAdj | ( | void | ) | [static] |
This function orders the list of adjacent nodes of all boundary nodes such that, for each reference boundary node, the adjacent node that has no adjacent counter-clockwise element will be the last one of the list of adjacent nodes of that reference node. It is assumed that the list of adjacent nodes of a reference node is ordered radially in counter-clockwise order around the node. The result of this ordering is that the first adjacent node of a boundary node will be the next one when traversing the mesh surface boundary in counter-clockwise order, i.e, in the same order of the furnished element nodal incidence.
Definition at line 946 of file pfs.c.
References NODE_INTERIOR, PfsSurf::nodelist, PfsSurf::numnodes, PFS_SUCCESS, pfsOrderBdryNodeAdj(), and PfsNode::type.
Referenced by pfsRCompleteSurf().

| static int pfsOrderBdryNodeAdj | ( | int | ref_id | ) | [static] |
Given an index of a boundary node, this function orders the list of adjacent nodes of this node such that the adjacent node that has no adjacent counter-clockwise element will be the last one. The adjacent node that has no adjacent counter-clockwise element is identified by the field elem = NULL. It is assumed that the given reference boundary node has at least two adjacent nodes and that the list of adjacent nodes is ordered radially in counter-clockwise order around the reference node. There can be only one adjacent node that has no counter-clockwise element when traversing the adjacent nodes radially around the reference node. If more than one is found, a non-manifold vertex situation would occur. If this is found, an invalid status is returned. Otherwise a valid status is returned.
Definition at line 873 of file pfs.c.
References PfsNode::adj_head, PfsAdjNode::elem, PfsAdjNode::next, PfsSurf::nodelist, PFS_NON_MANIFOLD_VERTEX, and PFS_SUCCESS.
Referenced by pfsOrderAllBdryNodeAdj().

| static int pfsParDerivCurElem | ( | double | u, | |
| double | v, | |||
| double * | xdu, | |||
| double * | ydu, | |||
| double * | zdu, | |||
| double * | xdv, | |||
| double * | ydv, | |||
| double * | zdv, | |||
| double * | xdw, | |||
| double * | ydw, | |||
| double * | zdw | |||
| ) | [static] |
Given the parametric space of a point that is presumably in the current element, this function returns the derivatives of cartesian coordinates with respect to the paramatric values at that point. It also returns a nodal interpolated normal vector as the third vector of the derivatives. If the given point is not inside the current element, it returns a false (0) status. Otherwise, it returns a true (1) status. In any case, it computes the parametric derivatives and normal vector at the given point assuming that it is inside the given element, i.e, using natural triangular (baricentric) interpolation of element nodes parametric derivatives. It is assumed that there is a defined current element.
Definition at line 2569 of file pfs.c.
References PfsElem::inc, pfsParGetAreaCoord(), pfsRItrNodeJacobian(), pfsRItrNodeNormal(), pfsRItrNodeParVals(), and TOLER.
Referenced by pfsRGetJacobian().
| static void pfsParGetAreaCoord | ( | double | u, | |
| double | v, | |||
| double * | un, | |||
| double * | vn, | |||
| double * | b0, | |||
| double * | b1, | |||
| double * | b2 | |||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 481 of file pfs.c.
References pfsArea2d().
Referenced by pfs3dPntCurElem(), pfsChkProxElemEdge(), pfsChkProxElemNode(), pfsParDerivCurElem(), pfsParPntCurElem(), and pfsParPntCurElemAttract().
| static int pfsParPntCurElem | ( | double | x, | |
| double | y, | |||
| double | z, | |||
| double * | u, | |||
| double * | v | |||
| ) | [static] |
This function returns the parametric values of a given point in cartesion space that is presumably in the current element. If the given point is not inside the current element, it returns a false (0) status. Otherwise, it returns a true (1) status. In any case, it computes the parametric coordinates of the given point assuming that it is inside the given element, i.e, using natural triangular (baricentric) interpolation of element nodes parametric coordinates. It is assumed that there is a defined current element.
Definition at line 2454 of file pfs.c.
References COL_TOLER, PfsElem::inc, pfs3dGetAreaCoord(), pfsParGetAreaCoord(), pfsRItrNodeCoords(), and pfsRItrNodeParVals().
Referenced by pfsRGetElem(), and pfsRProjectOn().
| static int pfsParPntCurElemAttract | ( | double * | x, | |
| double * | y, | |||
| double * | z, | |||
| double * | u, | |||
| double * | v | |||
| ) | [static] |
This function returns the parametric values of a given point in cartesion space that is presumably in the current element. If the given point is not inside the current element, it returns a false (0) status. Otherwise, it returns a true (1) status. In this case, it updates the point coordinates to avoid tolerance problems. In any case, it computes the parametric coordinates of the given point assuming that it is inside the given element, i.e, using natural triangular (baricentric) interpolation of element nodes parametric coordinates. It is assumed that there is a defined current element.
Definition at line 2372 of file pfs.c.
References COL_TOLER, PfsElem::inc, pfs3dGetAreaCoord(), pfsParGetAreaCoord(), pfsRItrNodeCoords(), and pfsRItrNodeParVals().
Referenced by pfsFinishFreeFaceShotLen(), pfsRShot(), and pfsUpdateShotLen().
| void pfsRActivateSurf | ( | void * | surf | ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
void pfsRActivateSurf( void *surf )
surf - pointer to the surface data to activate (in)
This function sets the given surface mesh (given by its pointer) as the current active one. All node and element data are inserted in the current active surface mesh. All iteration traversal of surface data is performed in the current active surface mesh.
Definition at line 3889 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by _surfaceSlide(), _surfaceToGlobal(), _surfaceToLocal(), and ConstSurfaceBuild().
| int pfsRAddElem | ( | int | v0, | |
| int | v1, | |||
| int | v2 | |||
| ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
void pfsRAddElem( int vt0, int vt1, int vt2 )
vt0 - index of first element node (in) vt1 - index of second element node (in) vt2 - index of third element node (in)
This function inserts of a new element (face) in the database of the current active surface. The elements are stored in a R-tree indexed by the 3D bounding boxe of each element. If there is no active surface it returns a false (0) status, otherwise it returns a true (1) status.
Definition at line 3957 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by ConstSurfaceBuild().

| int pfsRAddNode | ( | double | x, | |
| double | y, | |||
| double | z | |||
| ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
int pfsRAddNode( double x, double y, double z )
x, y, z - node coordinates (in)
This function inserts a new node in the database of the current active surface. If the current number of inserted nodes is equal to the current maximum number of nodes, the function doubles the maximum number of nodes and reallocates the node vector list. The function returns an index of the created node. This index ranges from 0 to the number of nodes - 1.
Definition at line 3922 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by ConstSurfaceBuild().

| int pfsRCompleteSurf | ( | void | ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
This functions finishes up the creation of the data structure of the current active surface mesh. It does the following:
Definition at line 3985 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by ConstSurfaceBuild().
| int pfsREval | ( | double | u, | |
| double | v, | |||
| double * | x, | |||
| double * | y, | |||
| double * | z | |||
| ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
int pfsREval( double u, double v, double *x, double *y, double *z )
u, v - parametric values of point (in) x, y, z - components of cartesian points (out)
This function returns the components of the cartesian points indicated by its parametric values. If there is no active surface it returns a false (0) status, otherwise it returns a true (1) status.
| void pfsRFreeSurf | ( | void * | surf | ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
void pfsRFreeSurf( void *surf )
surf - pointer to the surface mesh data to delete (in)
This function releases the memory used by the given surface.
Definition at line 3901 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by pfsRCompleteSurf().
| int pfsRGetElem | ( | double | x, | |
| double | y, | |||
| double | z, | |||
| void ** | elem | |||
| ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
void pfsRGetElem( double x, double y, double z, void **elem )
x, y, z - global point coordinates (in) elem - pointer to corresponding pfs element (out)
This function returns a true state if a pfs element is found for a given point, otherwise it returns a false status.
Definition at line 4300 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by _surfaceSlide(), _surfaceToGlobal(), and _surfaceToLocal().
| int pfsRGetJacobian | ( | double | u, | |
| double | v, | |||
| double * | xdu, | |||
| double * | ydu, | |||
| double * | zdu, | |||
| double * | xdv, | |||
| double * | ydv, | |||
| double * | zdv, | |||
| double * | xdw, | |||
| double * | ydw, | |||
| double * | zdw | |||
| ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
int pfsRGetJacobian( double u, double v, double *xdu, double *ydu, double *zdu, double *xdv, double *ydv, double *zdv, double *xdw, double *ydw, double *zdw )
u, v - parametric values of point (in) xdu, ydu, zdu - components of point jacobian matrix (out) xdv, ydv, zdv - components of point jacobian matrix (out) xdw, ydw, zdw - components of the normal vector of (out) element face where is the point
This function returns the components of the point jacobian matrix of the point indicated by its parametric values. If there is no active surface it returns a false (0) status, otherwise it returns a true (1) status.
| int pfsRGetLoopElem | ( | double | x, | |
| double | y, | |||
| double | z, | |||
| void ** | elem | |||
| ) |
--------------------------------------------------------------- /* Esta função retorna o elemento de um loop externo mais próximo ao ponto dado pelas coordenadas xyz
Definition at line 4324 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by _surfaceSlide(), _surfaceToGlobal(), and _surfaceToLocal().
| void* pfsRInitSurf | ( | int | maxnodes, | |
| int | maxelems | |||
| ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
void *pfsRInitSurf( int maxnodes, int maxelems )
maxnodes - maximum number of nodes of new mesh (in) maxelems - maximum number of elements of new mesh (in)
This function allocates the global list vectors of nodal and element data for a new mesh. The return value is a pointer to the created surface data structure.
Definition at line 3841 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by ConstSurfaceBuild().

| int pfsRItr3dBoundBox | ( | double * | xmin, | |
| double * | xmax, | |||
| double * | ymin, | |||
| double * | ymax, | |||
| double * | zmin, | |||
| double * | zmax | |||
| ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
int pfsRItr3dBoundBox( double *xmin, double *xmax, double *ymin, double *ymax, double *zmin, double *zmax )
xmin, xmax ymin, ymax zmin, zmax - returned bounding box (out)
This function returns the 3D bounding box of the current active surface mesh. If there is no active surface it returns a false (0) status, otherwise it returns a true (1) status. If a pointer parameter is null, the corresponding bounding box limit is not returned.
| void pfsRItrElem3dBox | ( | double * | xmin, | |
| double * | ymin, | |||
| double * | zmin, | |||
| double * | xmax, | |||
| double * | ymax, | |||
| double * | zmax | |||
| ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
void pfsRItrElem3dBox( double *xmin, double *ymin, double *zmin, double *xmax, double *ymax, double *zmax )
xmin, ymin, zmin - minimal components of element 3d bounding box (out) xmax, ymax, zmax - maximum components of element 3d bounding box (out)
This function returns the components of the 3d bounding box of current element (face) being traversed.
| void pfsRItrElemCenter | ( | double * | x, | |
| double * | y, | |||
| double * | z | |||
| ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
void pfsRItrElemCenter( double *x, double *y, double *z )
x, y, z - coordinates of element center (out)
This function returns the coordinates of the center of current element (face) being traversed.
Definition at line 4387 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by pfsRGetLoopElem().
| int pfsRItrElemNode | ( | int * | id | ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
int pfsRItrElemNode( int *id )
id - index of current node of element (out)
This function iterates on the nodes of the current element (face) being traversed. It returns the index of the current node of the current element. If there is no element in the database, if there is no active surface, if there is no other element to traverse, or if there is no more nodes in the element, the function returns an end of iteration status. Otherwise, it returns a success status.
Definition at line 4367 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by _surfaceCurrElemTransfMtx(), and _surfaceSlide().
| void pfsRItrElemNormal | ( | double * | nx, | |
| double * | ny, | |||
| double * | nz | |||
| ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
void pfsRItrElemNormal( double *nx, double *ny, double *nz )
nx, ny, nz - components of element normal vector (out)
This function returns the components of the normal vector of current element (face) being traversed.
Definition at line 4402 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by _surfaceCurrElemTransfMtx(), and _surfaceLocalT3Coord().
| void pfsRItrElemParBox | ( | double * | umin, | |
| double * | vmin, | |||
| double * | umax, | |||
| double * | vmax | |||
| ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
void pfsRItrElemParBox( double *umin, double *vmin, double *umax, double *vmax )
umin, vmin - minimal components of element parametric bounding box (out) umax, vmax - maximum components of element parametric bounding box (out)
This function returns the components of the parametric bounding box of current element (face) being traversed.
| int pfsRItrFirst3dElem | ( | double | xmin, | |
| double | xmax, | |||
| double | ymin, | |||
| double | ymax, | |||
| double | zmin, | |||
| double | zmax | |||
| ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
int pfsRItrFirst3dElem( double xmin, double xmax, double ymin, double ymax, double zmin, double zmax ) xmin, xmax ymin, ymax zmin, zmax - bounding box for search (in)
This function starts an iteration for traversal of elements (faces) within a given bounding box. It sets up the first element in the database within the bounding box as the current one for traversal. If there is no element in the database within the bounding box, or if there is no active surface, the function returns an end of iteration status. Otherwise, it returns a success status.
Definition at line 4187 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by pfsRProjectOn().
| int pfsRItrFirstElem | ( | void | ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
This function starts an iteration for traversal of elements (faces). It sets up the first element in the database as the current one for traversal. If there is no element in the database, or if there is no active surface, the function returns an end of iteration status. Otherwise, it returns a success status.
Definition at line 4139 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by pfsRGetElem().
| int pfsRItrFirstLoopNode | ( | int | loop_id, | |
| int * | id | |||
| ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
int pfsItrFirstLoopNode( int loop_id, int *id )
loop_id - index of target loop (in) id - index of first loop node (out)
This function starts an iteration for traversal of loop nodes. It returns the id of the first of a loop given by its id (loop_id). If there is no element in the database, or if there is no active surface, the function returns an end of iteration status. Otherwise, it returns a success status.
Definition at line 4524 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by pfsIsParPtInside(), pfsIsParPtOnBound(), pfsRGetLoopElem(), and pfsSnapParPtToBound().
| int pfsRItrFirstParElem | ( | double | umin, | |
| double | umax, | |||
| double | vmin, | |||
| double | vmax | |||
| ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
int pfsRItrFirstParElem( double umin, double umax, double vmin, double vmax ) umin, umax vmin, vmax - parametric bounding box for search (in)
This function starts an iteration for traversal of elements (faces) within a given parametric bounding box. It sets up the first element in the database within the parametric bounding box as the current one for traversal. If there is no element in the database within the bounding box, or if there is no active surface, the function returns an end of iteration status. Otherwise, it returns a success status.
Definition at line 4239 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by pfsREval(), and pfsRGetJacobian().
| int pfsRItrNext3dElem | ( | double | xmin, | |
| double | xmax, | |||
| double | ymin, | |||
| double | ymax, | |||
| double | zmin, | |||
| double | zmax | |||
| ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
int pfsRItrNext3dElem( double xmin, double xmax, double ymin, double ymax, double zmin, double zmax ) xmin, xmax ymin, ymax zmin, zmax - bounding box for search (in)
This function continues an iteration for traversal of elements (faces) within a given bounding box. It sets up the next element in the database within the bounding box as the current one for traversal. If there is no other element in the database within the bounding box, the function returns an end of iteration status. Otherwise, it returns a success status.
Definition at line 4214 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by pfsRProjectOn().
| int pfsRItrNextElem | ( | void | ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
This function continues an iteration for traversal of elements (faces). It sets up the next element in the database as the current one for traversal. If there is no element in the database, if there is no active surface, or if there is no other element to traverse, the function returns an end of iteration status. Otherwise, it returns a success status.
Definition at line 4164 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by pfsRGetElem().
| int pfsRItrNextLoopNode | ( | int | loop_id, | |
| int | ref_id, | |||
| int * | id | |||
| ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
int pfsItrNextLoopNode( int loop_id, int ref_id, int *id )
loop_id - index of target loop (in) ref_id - index of reference loop node (in) id - index of next loop node (out)
This function returns the id of the next boundary node after a given reference boundary node along a loop. If the loop of the given node is the surface outside loop, the returned node is the next one when traversing the surface boundary loop in counter-clockwise order when looking the surface from the side pointed to by the surface normals. If the loop is not the outside one, the traversal is done in clockwise order. If there is no element in the database, if there is no active surface, or if the given reference node is not a boundary node, the function returns an end of iteration status. Otherwise, it returns a success status.
Definition at line 4537 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by pfsIsParPtInside(), pfsIsParPtOnBound(), pfsRGetLoopElem(), and pfsSnapParPtToBound().
| int pfsRItrNextParElem | ( | double | umin, | |
| double | umax, | |||
| double | vmin, | |||
| double | vmax | |||
| ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
int pfsRItrNextParElem( double umin, double umax, double vmin, double vmax ) umin, umax vmin, vmax - parametric bounding box for search (in)
This function continues an iteration for traversal of elements (faces) within a given bounding box. It sets up the next element in the database within the parametric bounding box as the current one for traversal. If there is no other element in the database within the bounding box, the function returns an end of iteration status. Otherwise, it returns a success status.
Definition at line 4265 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by pfsREval(), and pfsRGetJacobian().
| void pfsRItrNodeCoords | ( | int | id, | |
| double * | x, | |||
| double * | y, | |||
| double * | z | |||
| ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
void pfsRItrNodeCoords( int id, double *x, double *y, double *z )
id - index of target node (in) x, y, z - coordinates of node (out)
This function returns the coordinates of the node indicated by its index.
Definition at line 4463 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by _surfaceCurrElemTransfMtx(), _surfaceLocalT3Coord(), pfs3dPntCurElem(), pfsDistPntCurElem(), pfsLoopShot(), pfsParPntCurElem(), and pfsParPntCurElemAttract().
| void pfsRItrNodeJacobian | ( | int | id, | |
| double * | xdu, | |||
| double * | ydu, | |||
| double * | zdu, | |||
| double * | xdv, | |||
| double * | ydv, | |||
| double * | zdv | |||
| ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
void pfsRItrNodeJacobian( int id, double *xdu, double *ydu, double *zdu, double *xdv, double *ydv, double *zdv )
id - index of target node (in) xdu, ydu, zdu - components of node jacobian matrix (out) xdv, ydv, zdv - components of node jacobian matrix (out)
This function returns the components of the nodal jacobian matrix of the node indicated by its index.
Definition at line 4487 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by pfsParDerivCurElem().

| void pfsRItrNodeNormal | ( | int | id, | |
| double * | nx, | |||
| double * | ny, | |||
| double * | nz | |||
| ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
void pfsRItrNodeNormal( int id, double *nx, double *ny, double *nz )
id - index of target node (in) nx, ny, nz - components of node normal vector (out)
This function returns the components of the normal vector of the node indicated by its index.
Definition at line 4475 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by pfsParDerivCurElem().

| void pfsRItrNodeParVals | ( | int | id, | |
| double * | u, | |||
| double * | v | |||
| ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
void pfsRItrNodeParVals( int id, double *u, double *v )
id - index of target node (in) u, v - parametric values of node (out)
This function returns the surface parametric values of the node indicated by its index.
Definition at line 4503 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by _surfaceSlide(), pfs3dPntCurElem(), pfsChkProxElemEdge(), pfsChkProxElemNode(), pfsIsParPtInside(), pfsIsParPtOnBound(), pfsParDerivCurElem(), pfsParPntCurElem(), pfsParPntCurElemAttract(), pfsShotXLine(), and pfsSnapParPtToBound().
| int pfsRItrNumLoops | ( | void | ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
int pfsItrNumLoops( void )
This function returns the total number of loops (connected boundary portion) of current active surface mesh.
Definition at line 4514 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by pfsIsParPtInside(), pfsIsParPtOnBound(), pfsRGetLoopElem(), and pfsSnapParPtToBound().
| int pfsRItrNumNodes | ( | void | ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
This function returns the total number of nodes of current active surface mesh.
| int pfsRItrParBoundBox | ( | double * | umin, | |
| double * | umax, | |||
| double * | vmin, | |||
| double * | vmax | |||
| ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
int pfsRItrParBoundBox( double *umin, double *umax, double *vmin, double *vmax )
umin, umax vmin, vmax - returned parametric bounding box (out)
This function returns the parametric bounding box of the current active surface mesh. If there is no active surface it returns a false (0) status, otherwise it returns a true (1) status. If a pointer parameter is null, the corresponding bounding box limit is not returned.
| int pfsRProjectOn | ( | double | x, | |
| double | y, | |||
| double | z, | |||
| double * | u, | |||
| double * | v | |||
| ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
int pfsRProjectOn( double x, double y, double z, double *u, double *v )
x, y, z - coordinates of point (in) u, v - parametric values of point (out)
This function returns the surface parametric values of the point indicated by its coordinates. If there is no active surface it returns a false (0) status, otherwise it returns a true (1) status.
| void pfsRSetCurrElem | ( | void * | elem | ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
void pfsRSetCurrElem( void *elem )
elem - pointer to target element (in)
This function sets up the given target element as the current element for consulting data.
Definition at line 4289 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by _surfaceSlide(), _surfaceToGlobal(), _surfaceToLocal(), pfsLoopShot(), pfsRShot(), and pfsShotSolve().
| int pfsRShot | ( | void * | init_elem, | |
| double | x0, | |||
| double | y0, | |||
| double | z0, | |||
| double | u_shot, | |||
| double | v_shot, | |||
| double | len, | |||
| void ** | end_elem, | |||
| double * | x1, | |||
| double * | y1, | |||
| double * | z1 | |||
| ) |
Esta função calcula a posição final de um tiro no espaço cartesiano navegando através do espaço paramétrico.
| init_elem | (in) elemento a partir do qual foi dado o tiro | |
| x0,y0,z0 | (in) posição inicial do tiro no espaço cartesiano | |
| u_shot,v_shot | (in) direção do tiro no espaço paramétrico | |
| len | (in) comprimento do caminho que deve ser percorrido no espaço cartesiano | |
| end_elem | (out) elemento onde parou o tiro | |
| x1,y1,z1 | (out) posição final do tiro no espaço cartesiano |
Definition at line 4751 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by _surfaceSlide().
| void pfsRSolveSurfPar | ( | int | maxnumiter | ) |
---------------------------------------------------------------
void pfsRSolveSurfPar( int maxnumiter )
maxnumiter - maximum number of iterations (in)
This function computes by a Gauss-Seidel iterative scheme the surface parametric values of all nodes of the mesh in current active surface. It is assumed that the parametric values of all nodes have been initialized. If the given parameter for maximum number of iterations is null, the solution iterates until convergence is achieved (within a specified tolerance).
Definition at line 4053 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by ConstSurfaceBuild().

| static int pfsShotSolve | ( | PfsElem * | init_elem, | |
| double | u0, | |||
| double | v0, | |||
| PFSGeoPoint | p0, | |||
| double | u_shot, | |||
| double | v_shot, | |||
| PfsElem ** | end_elem, | |||
| double * | u1, | |||
| double * | v1, | |||
| PFSGeoPoint * | p1, | |||
| int * | type, | |||
| int * | ni, | |||
| int * | nj, | |||
| double * | len | |||
| ) | [static] |
Esta função determina a posição final do tiro de maneira recursiva. A cada passo é determinado o ponto de interseção do tiro com os elementos da malha adjacentes à posição inicial, sendo q conforme o tipo, a busca pelo ponto de interseção mais próximo é feita de forma diferenciada. A cada passo é verificado se o comprimento do caminho q deve ser percorrido já foi percorrido, o q satisfaz a condição de parada. Caso contrário, a busca continua e a informação de saída de um passo é a entrada para o próximo.
| init_elem | (in) elemento a partir do qual foi dado o tiro | |
| u0,v0 | (in) posição inicial do tiro no espaço paramétrico | |
| p0 | (in) posição inicial do tiro no espaço cartesiano | |
| u_shot,v_shot | (in) direção do tiro no espaço paramétrico | |
| end_elem | (out) elemento onde parou o tiro | |
| u1,v1 | (out) posição final do tiro no espaço paramétrico | |
| p1 | (out) posição final do tiro no espaço cartesiano | |
| type | (in/out) classificação do tiro em relação à posição do seu pto de partida, ou seja, se está sobre nó, aresta, face | |
| ni | (in/out) qdo type é NODE representa o índice do nó sobre o qual está o pto de partida. Qdo EDGE é um dos nós da aresta | |
| nj | (in/out) Indice do outro nó da aresta | |
| len | (in/out) comprimento do caminho que deve ser percorrido no espaço cartesiano |
Definition at line 3756 of file pfs.c.
References _loop_, EDGE, FACE, FREE_FACE, LOOP, NODE, pfs3dPntCurElem(), pfsEdgeShot(), pfsFaceShot(), pfsFinishFreeFaceShotLen(), pfsLoopShot(), pfsNodeShot(), pfsRSetCurrElem(), pfsUpdateShotLen(), PFSGeoPoint::x, PFSGeoPoint::y, and PFSGeoPoint::z.
Referenced by pfsRShot().
| static int pfsShotXLine | ( | PfsElem * | elem, | |
| double | u0, | |||
| double | v0, | |||
| double | u_shot, | |||
| double | v_shot, | |||
| int | na, | |||
| int | nb, | |||
| double * | u1, | |||
| double * | v1, | |||
| int * | type, | |||
| int * | n_inter | |||
| ) | [static] |
This function computes the 2D (parametric) coordinates of the intersection point of a semi-infinite (shot) line and an edge (ab).
| elem | - edge´s element (in) | |
| u0,v0 | - param. coords. of starting pt of shot line (in) | |
| u_shot | v_shot - shot line parametric direction vector (in) | |
| na,nb | - edge nodes (in) | |
| u1,v1 | - parametric coordinates of intersectionpt. (out) | |
| type | - type of intersection pt, wheither node or edge (out) | |
| n_inter | - the node intersecepted (out) |
Definition at line 3103 of file pfs.c.
References EDGE, NODE, pfsChkProxElemNode(), pfsRItrNodeParVals(), size, X_CROSS_LINE_SHOT, and Y_CROSS_LINE_SHOT.
Referenced by pfsEdgeShot(), pfsFaceShot(), pfsLoopShot(), and pfsNodeShot().
| static int pfsSnapParPtToBound | ( | PFSGeoSurfPar * | p | ) | [static] |
This function attracts a given surface parametric point to the closest point on surface boundary.
Definition at line 2854 of file pfs.c.
References PFS_SUCCESS, pfsClstPtParLine(), pfsRItrFirstLoopNode(), pfsRItrNextLoopNode(), pfsRItrNodeParVals(), pfsRItrNumLoops(), PFSGeoSurfPar::u, and PFSGeoSurfPar::v.
Referenced by pfsSnapToBound().
| int pfsSnapToBound | ( | double * | u, | |
| double * | v, | |||
| double | toler | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 4609 of file pfs.c.
References Len2, pfsSnapParPtToBound(), PFSGeoSurfPar::u, and PFSGeoSurfPar::v.
| static void pfsSolve2x2 | ( | double | a[2][2], | |
| double | b[2], | |||
| double * | u, | |||
| double * | v | |||
| ) | [static] |
This function returns the solution of a 2 by 2 system of equations.
Definition at line 1929 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by pfsSolveSurfPar1Pass().

| static int pfsSolveSurfPar1Pass | ( | void | ) | [static] |
This function processes one entire pass of solution iterations, looping once on the list of nodes, to compute surface parametric values of nodes of the mesh in current active surface. It is assumed that the parametric values of all nodes have been initialized. The order of nodes to operate the iterative solution is stored in the solution order vector of the active surface. It is assumed that this vector has been created. The solution iteration never changes the parametric values of the reference node (the origin of parametric space). In each iteration, a local solution of the conformal mapping problem is performed at a node. A 2 by 2 system of equations is assembled in which the equation coefficients correspond to the conformal map coefficients of the node and the forcing vector is obtained from the current parametric values and coefficients of all the adjacent nodes. The solution of the system of equation furnishes the new parametric values of the node. It returns a flag indicating whether at least one parametric value has been updated. If the return flag is false (0), this means that the iterative solution has converged within the specified tolerance.
Definition at line 1968 of file pfs.c.
References ABS, PfsNode::adj_head, PfsNode::AtA, PfsAdjNode::AtA, PfsAdjNode::id, PfsSurf::iter_toler, PfsAdjNode::next, PfsSurf::nodelist, PfsSurf::numnodes, PfsNode::par, pfsSolve2x2(), PfsSurf::sol_order, PFSGeoSurfPar::u, and PFSGeoSurfPar::v.
Referenced by pfsRSolveSurfPar().
| static void pfsUnmarkLoopNodes | ( | int | ref_id | ) | [static] |
This function unmarks all the boundary nodes of a boundary loop. A boundary loop in this context is the loop that contains the given boundary node (given by its id). It traverses the boundary loop of the given node and sets the type of each viisted loop as NODE_BOUNDARY. The traversal along the nodes of a boundary loop uses the node-node adjacency relationship. Since the list of adjancent nodes of each boundary node is ordered in such a way that the first adjacent node has a free face (not an element) preceeding the node in counter-clockwise order around a reference node, the first adjacent node of the reference node will be the next boundary along the boundary loop.
Definition at line 1002 of file pfs.c.
References PfsNode::adj_head, NODE_BOUNDARY, NODE_MARKED, PfsSurf::nodelist, and PfsNode::type.
Referenced by pfsBuildLoopList().

| static int pfsUpdateShotLen | ( | double | u0, | |
| double | v0, | |||
| PFSGeoPoint * | p0, | |||
| double * | u1, | |||
| double * | v1, | |||
| PFSGeoPoint * | p1, | |||
| double * | len | |||
| ) | [static] |
Esta função atualiza o comprimento de caminhamento no espaço cartesiano a ser percorrido ao longo de um segmento da semi-linha de tiro no espaço paramétrico. A função calcula a distância no espaço cartesiano entre o ponto inicial no espaço paramétrico (u0,v0) e o ponto final no espaço paramétrico (u1,v1) na linha de tiro. Se a distância for inferior, o valor do comprimento de caminhamento ao longo da semi-linha é decrescido do valor da distância e a função retorna um status falso (0) indicando que ainda há comprimento para pagar ao longo do tiro. Se a distância for igual ou superior ao comprimento de caminhamento, calcula o ponto ao longo do último segmento de linha de tiro que corresponde ao comprimento de caminhamento que falta pagar e retorna um status verdadeiro (1) indicando que o percorrimento ao longo do tiro terminou. Em todos os casos são retornadas as coordenadas paramétricas e cartesianas do ponto no final do segmento percorrido da semi-linha de tiro.
| u0,v0 | (in) posição inicial do tiro no espaço paramétrico | |
| p0 | (in) posição inicial do tiro no espaço cartesiano | |
| u1,v1 | (in/out) posição final do tiro no espaço paramétrico | |
| p1 | (in/out) posição final do tiro no espaço cartesiano | |
| len | (in/out) comprimento do caminho que deve ser percorrido no espaço |
Definition at line 3597 of file pfs.c.
References _loop_, pfs3dPntCurElem(), pfs_node, PFSGeoDiffVec(), PFSGeoProdScalVec(), PFSGeoSumVec(), PFSGeoVecLen(), PFSGeoVecNormalize(), pfsParPntCurElemAttract(), TOLER, PFSGeoPoint::x, PFSGeoPoint::y, and PFSGeoPoint::z.
Referenced by pfsShotSolve().
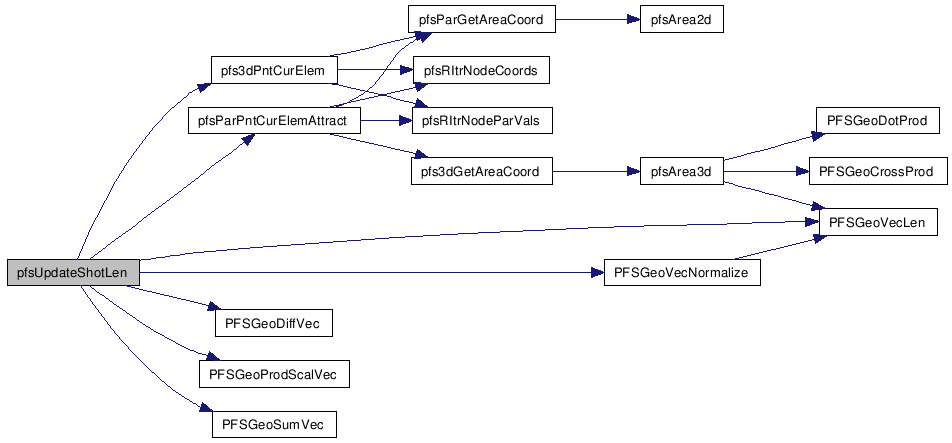
| int _loop_ = 0 |
int cur_elemnode [static] |
Definition at line 347 of file pfs.c.
Referenced by pfsRItrElemNode(), pfsRItrFirst3dElem(), pfsRItrFirstElem(), pfsRItrFirstParElem(), pfsRItrNext3dElem(), pfsRItrNextElem(), pfsRItrNextParElem(), and pfsRSetCurrElem().
PfsElem* curr_ielem = NULL [static] |
 1.5.3
1.5.3